Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Class 12 Numerical Chapter 9
Question:
An equi-convex lens has a focal length that is equal to half of the radius of curvature on either face. What is the refractive index of the lens’s construction material?
Solution:
Given Focal length, f=R
Let R1=R and R2=-R for an equi-convex lens.
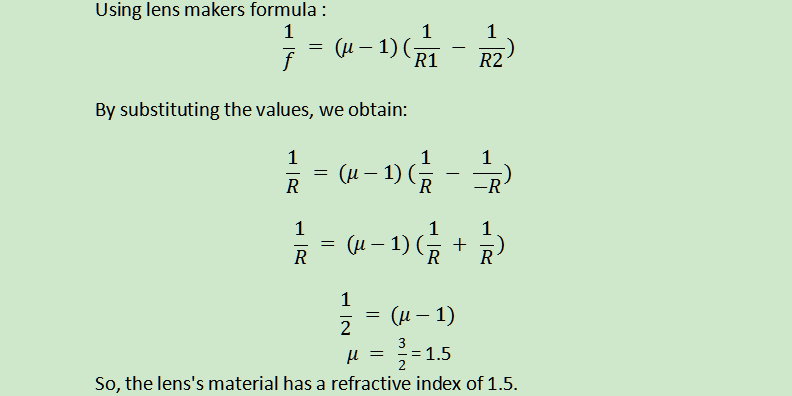
Question:
A concave lens with a refractive index of 1.5 is submerged in a medium with a refractive index of 1.65. What kind of lens is it?
Solution:
Concave lenses act like convex lenses if their relative refractive indices are less than 1.
Given,
n1=1.65, ng=1.5
Calculating the relative refractive index is as follows:
1ng = ng/n1 < 1 [As, n1 > ng]
Since the lens’s relative refractive index is less than 1, it will act like a convex lens.
Question:
How much power and focus length does a plane glass have?
Solution:
The inverse of optical power, focal length is a measure of how strongly an optical system converges or diverges light. A system with a positive focal length is said to converge light, whereas one with a negative focal length is said to diverge light. So, Power (P) = 1/f.
Since the angle of incidence and emergence with a shift are equal in a plane glass slab, the focal length of a planar surface is infinite. As a result, the rays will collide at infinity, giving them an infinite focal length.
Question:
How does the deviation of light depend on wavelength?
Solution:
The distance between two successive crests or troughs of a wave is known as its wavelength. It is measured in the wave’s direction.
The wavelength has an inverse relationship with the light’s deviation. The light that deviates the greatest has the shortest wavelength.
The letters of the word VIBGYOR are arranged in increasing order of the wavelengths of the many light colors. In other words, Red has the longest wavelength whereas Violet has the shortest.
Question:
Which light does a prism deviated more, blue or red, out of? Give an explanation.
Solution:
The wavelength of light, which is inversely proportional to the equivalent refractive index for that light in medium, determines how light in a medium deviates.
Blue light deviates more in a medium than red light does because blue light’s shorter wavelength results in a higher refractive index, which increases the amount of deviation that is created. Red light’s maximal wavelength corresponds to its lowest refractive index, which results in the least amount of deviation.
Question:
An equilateral prism allows light to travel through it with angles of incidence and emergence that are each equal to 3/5 of the prism’s angle. How much of a divergence is there?
Solution:
Let, Angle of prism = X
Angle of incident i= Angle of emergence e = X
Since prism is equilateral X = 60
So, i = e = 60 x 3/5 = 36
According to prism formula,
Angle of deviation d = i + e – X = 36+36 – 60 = 72 – 60 = 12 degree.
Question:
A reflecting or refracting type of telescope can be used for astronomy. What produces the higher-quality image between the two? Defend your response.
Solution:
Mirror has a strong resolving strength and no chromatic or spherical aberrations.
Question:
What is Refractive Index?
Solution:
Refractive index is the difference between the speed of light in a vacuum and another medium.
The measurement of how much a light ray bends when moving from one medium to another is called the refractive index. It is also known as n = c/v, which is the ratio of the speed of a light beam in a vacuum to that of a light ray in a substance.
Where,
n is the refractive index.
The speed of light in a vacuum is 3 108 m/s, therefore c
In a substance, v represents the speed of light.
Question:
When violet light instead of red light is incident on a lens, how does the focal length of the lens change? Justify your response.
Solution:

Question:
What circumstances cause a glass biconvex lens with a specific refractive index to behave as a plane glass sheet when submerged in a liquid?
Solution:

Question:
A concave lens or diverging-like behavior is displayed by the air bubble inside water. Why?
Solution:
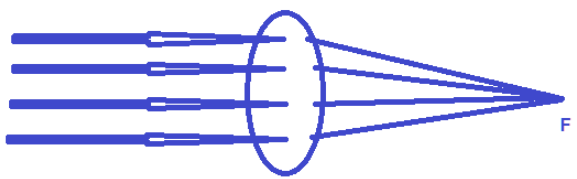
There are two categories of lenses: converging lenses and diverging lenses.
Converging lens: A lens that creates a true image by converting parallel light beams into convergent light rays. It is also depicted in the figure as:
Diverging lens: A lens that diverges light beams from parallel directions to create a virtual image is known as a diverging lens. Figures also show it to be:
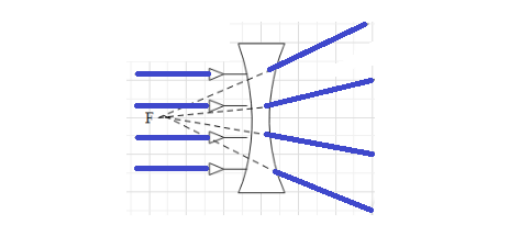
The diverging lens also causes light to be refracted and functions similarly to a concave lens. As a result, taking the air bubble as an example, a light beam is refracted as it travels through the bubble since the medium of transit has changed.
Since water is a denser medium than air, light rays in it diverge from the norm and can thus be compared to diverging lenses. The figure below illustrates this.
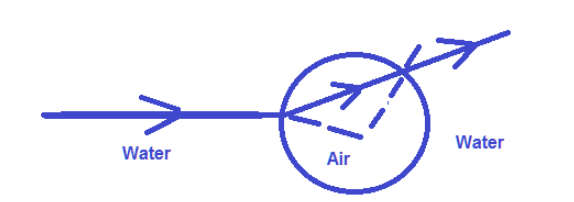
We can therefore conclude from this that an air bubble submerged in water behaves like a diverging or concave lens.
